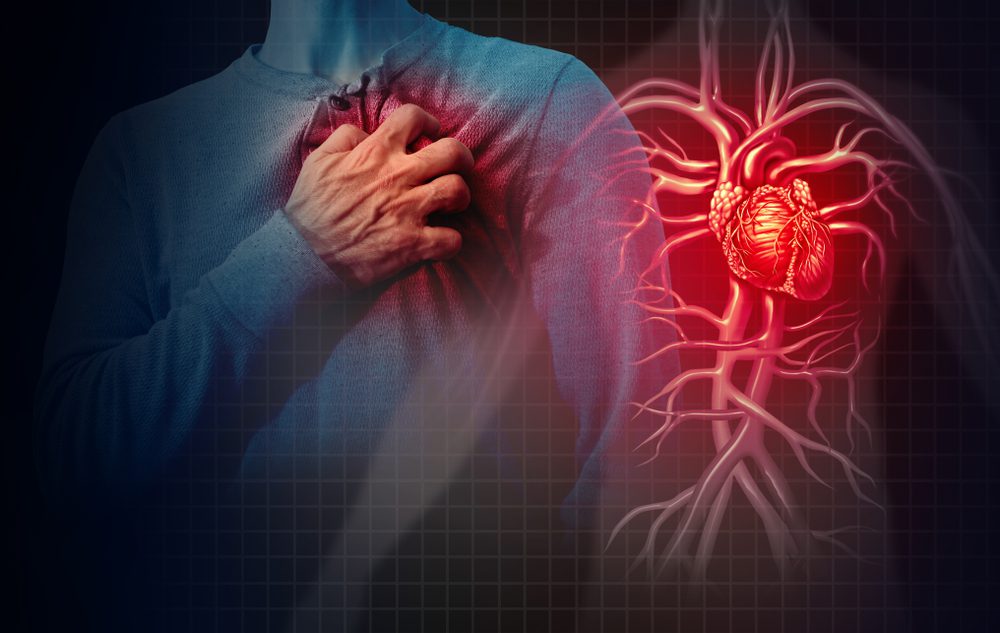
Chest pain is often associated with a heart attack; however, that’s not always the case. Experiencing sharp pain in your chest could be caused by many health problems. Because this symptom is also connected to respiration, digestion, and many other mental and physical health aspects, you shouldn’t think only of heart attacks.
One thing is certain: no matter the root cause, chest pain is always a serious medical concern. Even when it’s mild, seek medical health as soon as possible. Causes of chest pain are generally medical emergencies, so even if it goes away by itself in a matter of seconds or minutes, you should still inform your doctor about it.
However, if the pain is accompanied by nausea, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, as well as a cold sweat, don’t have second thoughts! All these symptoms indicate a heart attack. Call 911 immediately and bear in mind that a heart attack could also come with pain in the jaw, back, arms or neck.
Let’s dive into the possible causes of your chest pain!
Heart-related cause: Angina
People with angina describe their chest pain as a pressure or more like a strange feeling of the heart being squeezed. This type of chest pain happens when blood supply that flows to the heart muscle is drastically reduced. Right now, more than 9 million Americans are affected by angina.
Apart from a sensation of pressure in your chest, you may also experience:
- dizziness
- pain somewhere in the upper body
- burning in the shoulder (usually the left one)
Although they are quite different, people tend to confuse angina with a heart attack. For instance, angina doesn’t lead to heart tissue permanent damage like a heart attack does. Plus, there are actually two totally different types of angina, namely stable and unstable.
As the name suggests, the first chest pain is predictable, and it occurs when you’re performing certain physical activities, such as intense workouts. Stable angina appears when the heart pumps harder than normal.
Unstable angina occurs anytime. You can have it even when you’re just sitting on the couch, watching a movie. That’s why unstable angina is more serious than stable one. It actually suggests that your risk of having a heart attack is almost imminent.
However, no matter what type of angina you might experience, call 911.
Heart-related cause: heart attack
The chest pain caused by an ongoing heart attack is described by most patients as a sharp pain like someone is stabbing you right in your chest. A heart attack happens when one (or more) artery that’s responsible for supplying blood to your heart muscle is blocked.
As a result, if your heart muscle is deprived of oxygen-rich blood, its response will be severe pain. This happens with all muscles. In addition to sharp pain, some people may also experience the following:
- nausea
- lightheadedness
- irregular pulse
- shortness of breath
- a cold sweat
- sudden weakness
- a feeling of choking
- numbness in arm
There’s no need to mention that a heart attack is always a medical emergency… But, your response to it is crucial. The sooner you call for medical attention, the better.
Heart-related cause: Myocarditis
Myocarditis chest pain is often referred to as a mild one or a strange feeling of pressure. In certain cases, this pain appears due to heart muscle inflammation, which is often caused by a viral infection. Each year, there are approximately 1.5 million myocarditis cases worldwide.
Along with a feeling of pressure, you may also have:
- shortness of breath
- heart palpitations
- swollen legs
When the symptoms for this type of chest pain are mild or almost nonexistent, you should make an appointment with your doctor soon, but if the symptoms are severe, call 911 immediately.
Heart-related cause: Pericarditis
Patients with pericarditis reported dull pain as the most common symptom. In general, this type of pain occurs in the center of your chest. However, some people feel it on the left side. Essentially, pericarditis is inflammation of the heart, and in the vast majority of cases, the root cause is unknown.
Some doctors think that bacterial or viral infections may cause pericarditis. When compared to myocarditis, pericarditis refers to the inflammation of the sac that covers the heart.
Another important thing about this health condition is that it’s not common at all. In fact, it affects about 0.1% of hospital admissions.
Other pericarditis symptoms include:
- mild fever
- tiredness
- muscle ache
With proper rest and certain medications, pericarditis symptoms usually vanish in one or two weeks.
Heart-related cause: Aortic aneurysm
The scary part of an aortic aneurysm is that it may not cause any noticeable symptoms. In some cases, patients reported tenderness to touch, but nothing to raise any concerns.
As the name says, this condition happens in the aorta, the artery that’s responsible for carrying blood from your heart to blood vessels. That blood can lead to a bulge formation that looks like a balloon. Well, the formation is actually called an aortic aneurysm.
If you do spot any signs and symptoms, they may be the following:
- shortness of breath
- coughing
- tenderness in the check or abdomen (sometimes in the back)
Contact your doctor ASAP if you spot the slightest change in your breathing along with tenderness in the chest when touched.
Heart-related cause: Aortic dissection or Rupture
We know… the name itself sounds really bad, and everything is actually linked to aortic aneurysms. How so? Because an aortic aneurysm can eventually lead to an aortic dissection. It is basically a split within aortic layers that are responsible for letting blood leak out.
On top of that, it can also rupture, meaning that it can cause blood to burst from the aorta. Rupture symptoms may include:
- pain in your jaw, arms, or neck
- difficulty breathing
- constant and severe pain in your chest (sometimes in the upper back too)
Do not ignore these signs and symptoms! Aortic dissection or rupture is a serious health condition that should be treated immediately.
Heart-related cause: Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy patients reported moderate pain after performing a physical activity or eating. This condition causes the heart’s muscle to become thin; therefore, the pumping ability might be seriously affected.
In general, cardiomyopathy develops due to another health condition, or it might even be inherited.
Fortunately, its symptoms are pretty obvious:
- irregular heart rhythm
- shortness of breath
- swollen legs and ankles
- heart palpitations
If you think that something unusual is going on (especially if you have chest pain), call your doctor.
Heart-related cause: Valve Disease
The type of pain felt in the chest that comes due to valve disease is described as a feeling of intense pressure. Valve disease is common among the elderly. As we age, the risk of developing valve disease increases significantly.
The symptoms of valve disease depend on what valve is affected. Below you’ll find all of them.
- shortness of breath
- tiredness
- pressure in the chest
- heart murmur
Usually, valve disease is not an emergency, but the sooner you inform your doctor, the better.
Respiratory cause: Pulmonary Embolism
The first entry on our list when it comes to respiratory causes is pulmonary embolism (PE). The pain associated with it can be either gradual or sudden. Many patients reported a sharp pain, such as the pain experienced when a heart attack occurs.
PE is basically a blood clot stuck in an artery that’s found in one of your lungs. People with pulmonary embolism have difficulties breathing, and this awful experience can come all of a sudden.
Other symptoms associated with pulmonary embolism include:
- swollen legs
- severe coughing accompanied by a mix of mucus and blood
Seek immediate help if you experience any of these. A pulmonary embolism can be fatal!
Respiratory cause: Collapsed Lung
People with collapsed lung experience pain when they inhale. Also known as pneumothorax, collapsed lung happens when air gets stuck between the chest wall and the lungs.
When you inhale, your lungs expand, and the buildup of air found near them can put a lot of pressure on these essential internal organs.
Pneumothorax is usually caused by an injury such as a car accident or gunshot. But it can also happen due to rib fracture. If any of these happened to you and it feels impossible to inhale and exhale normally, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Respiratory cause: Pneumonia
Stabbing pain is usually felt by pneumonia patients when they inhale, and it often occurs due to a flu complication or any other respiratory infection. If left untreated, the pain becomes unbearable. And chest pain is not the only symptom. Patients may also experience the following:
- fever
- coughing
- chills
Do you feel pain while inhaling? If the answer is yes, talk to your doctor immediately, especially if you’re also coughing up blood.
Respiratory cause: Asthma
The type of chest pain associated with asthma is tightness in the chest. This is pretty obvious since asthma is a health condition that leads to inflammation in your airways. During asthma flare-ups, patients may also experience wheezing and trouble breathing.
Thankfully, asthma can be easily controlled with certain medications, but, if you think that your inhaled medications aren’t working as they should be, contact your doctor.
Respiratory cause: COPD
Chronic obstructive lung disease a.k.a. COPD is a condition in which you deal with inflamed airways. The chest pain linked to COPD is described as a feeling of tightness that often gets worse when performing physical activities.
People with COPD deal with the following symptoms:
- coughing
- wheezing
- chest tightness
If you notice any of these, seek medical help as soon as possible!
Respiratory cause: Pleurisy
If you have chest pain that gets worse when breathing or coughing, call 911 ASAP!
As the name suggests, pleurisy is a health condition that refers to pleura. Pleura is actually the tissue layer that covers the lungs and the tissue lining found in the inner wall of the chest cavity. When this membrane becomes inflamed, doctors will most definitely tell their patients that they are dealing with pleural disease or pleurisy.
Its symptoms include:
- coughing
- sharp chest pain
- shortness of breath
Note that the pain may go through the upper body and it can turn into an ache.
Respiratory cause: Lung Cancer
Sudden chest pain with virtually no apparent symptom could have the worst possible outcome. The constant growth of abnormal cells in the lungs translates to cancer. This type of cancer affects the function of your lungs, making it harder to breathe.
Other lung cancer symptoms include:
- chest pain that has nothing to do with coughing
- chest pain that gets worse when breathing, coughing, or laughing
- shortness of breath
All of the above should concern you. If you experience any of them, you might want to go to the hospital.
Respiratory cause: Pulmonary Hypertension
Pressure felt in the chest is commonly associated with pulmonary hypertension, according to the American Heart Association. Sadly, pulmonary hypertension can lead to heart failure. In its early stages, you will most likely have difficulty breathing, especially while exercising.
However, you can also experience the following:
- swollen legs
- racing heartbeat
- fainting
Certain lifestyle changes and proper medication can treat pulmonary hypertension. If you think that something’s going on, ask for an evaluation.
Digestive cause: GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, commonly referred to as GERD, is a serious health condition that should not be ignored. People with GERD report a burning sensation in the chest as an early symptom of the disease.
Due to GERD, patients may also experience trouble swallowing and a strange feeling of having something stuck in their throats. And while its symptoms don’t actually require a hospital trip, you should most definitely tell your doctor about them.
Digestive cause: Esophagitis
Esophagitis might be confused with GERD because a burning sensation is also felt in its case, but this condition can actually appear due to GERD. Esophagitis is a condition in which the tissue found in the esophagus gets inflamed.
So, if you’re dealing with an unpleasant sensation when swallowing, talk to your doctor. You might have esophagitis or, even worse, GERD without realizing it.
Digestive cause: Esophageal rupture
The chest pain connected to esophageal rupture is described as mild to severe, and it often comes like lightning (quick and unexpected).
Along with chest pain, people may also experience the following:
- fever
- nausea
- vomiting
- rapid breathing
The above symptoms require immediate medical help. So do not hesitate! Call 911 as soon as you can.
Digestive cause: PEMDs
Primary esophageal motility disorders, also known as PEMDs, refer to many different disorders related to the esophagus. The chest pain that comes from them is usually mild; people say that it feels like heartburn.
If you have PEMDs, you may experience the following symptoms:
- difficulty swallowing
- an unusual sensation that what you’re eating is stuck in your esophagus
See your doctor if you experience any of these. Medications can ease swallowing; however, a surgical procedure may also be required.
Digestive cause: Dysphagia
Dysphagia is referred to as an unpleasant sensation that happens every single time when swallowing. It is a condition in which the esophagus is affected, causing coughing and chest pain.
So, if you notice any swallowing issues, call your doctor, as dysphagia has a wide range of root causes. Usually, it is treated by taking certain meds or by going to physical therapy.
Digestive cause: Gallstones
If the other digestive causes often come with mild chest pain, that’s not the case of gallstones. People with gallstones experience intense pain in their chests that usually starts from the upper abdomen, migrating to the chest area.
The pain is the result of blocked gallstones in the bile duct and is often mentioned by doctors as a gallbladder attack. The symptoms tend to occur after eating large-sized portions, and they include:
- fever
- vomiting
- color changes in the urine and/or stools
So, if you’re used to associating a heavy meal with chest pain, note that it’s not normal at all, and you should seek medical help.
Digestive cause: Pancreatitis
Do you experience a pain that starts from the upper abdomen and goes to your chest and back? If yes, you might have pancreatitis. The inflammation of the pancreas is called pancreatitis, and it can be chronic or acute.
The latter one, namely acute pancreatitis, is usually temporary, but the chronic one is there to stay. Chronic pancreatitis leads to irreversible damage to your pancreas, and the common signs of it are vomiting and diarrhea. Due to its symptom, patients experience unwanted weight loss.
Digestive cause: Hiatal Hernia
Pain in both the abdomen and chest is experienced by people with hiatal hernia. Hiatal hernias happen when the stomach starts to expand through the opening of the diaphragm called hiatus, where the esophagus normally passes before connecting with the stomach.
The symptoms of hiatal hernia are the following:
- vomiting (sometimes with blood)
- having black stools
- heartburn
If any of these occur to you, make an appointment immediately.
Mental health-related cause: Anxiety Attack
Anxiety attacks are no joke at all. The chest pain associated with it is often described as a needle-like pain. However, people who have anxiety attacks may also experience sweating, difficulty breathing, sweating, lightheadedness, nausea, as well as heart palpitations.
And although the vast majority of them are also heart attack symptoms, people shouldn’t confuse them. When it comes to anxiety attacks, the pain associated is a needle-like feeling, while heart attacks seem to feel more like a pressure-like sensation.
When an anxiety attack strikes, the person who experiences it is most likely really nervous. Try to calm down and relax. Think about something positive and stress-free! If nothing helps, contact a psychologist.

Mental health-related cause: Panic Attack
Experiencing stabbing pain is often reported as a panic attack symptom. Accompanied by difficulty breathing and rapid heartbeat, panic attacks occur all of a sudden. And although it’s a short-term event (a couple of minutes), it can be tragic in certain scenarios, such as driving your car.
Panic attacks have many symptoms, but the most common ones include:
- a racing heart
- chest pain
- trouble breathing
- dizziness
Doctors generally recommended psychological therapy.
No matter the cause of your chest pain, you should see your doctor if you aren’t feeling well. It’s always better to be safe than sorry. If you found this article helpful, we also recommend reading: 11 Genetic Diseases You Can Easily Get Tested For